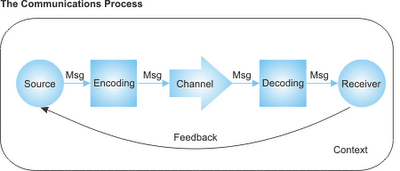
Communication is the transfer of information from a source to a receiver.
Communication is a vital part of the human experience. It enables the passing on and sharing of information and is necessary for survival. Humans must communicate in order to express/convey their interests, wants, needs and desires. Consider a newly born baby who cannot yet speak. He or she cries to express hunger, sleepiness or discomfort. Likewise, when happy he or she will coo or smile.
We may now conclude that communication is an inborn/innate and therefore inevitable part of being human. Consider this story:
The Story of Djuma (The Wolf Boy)
Djuma was found in 1962 at the age of 7 in the company of wolves. He walked on all fours like a wolf, bit like a wolf, ate raw meat and howled like a wolf. He was a victim of civil unrest in Russia whereby all his family members were killed and he was somehow found and raised by wolves. This story brings out the point that human beings need to communicate by whatever means necessary. This story also alludes to the fact that human beings are not the only beings that can communicate. Most animals possess some kind of communication system. For example, spiders and crabs have a complex communication system for courtship and mating. The bees also have a complex communication system for alerting other bees to a newly found food source.
None the less, human beings are said to have the superior communication system, characterized by the use of language and gestures in a systematic way. Zeuschner (1994) defines this communication as ‘the process of people interacting through the use of messages.’

No comments:
Post a Comment